Adult Services

Voice
There are a number of reasons why some people have difficulty with their voice..

Swallowing
Conditions that result in difficulty swallowing can be helped..

Stroke
Stroke can result in aphasia, dysarthria, apraxia or a combination..
Voice
When people have difficulty with their voice, the voice may become hoarse and gravelly, a soft whisper or people may have no voice at all.
There are a number of causes of voice disorders.
A speech-language pathologist will work closely with the treating physician. Once the cause has been diagnosed and medical intervention complete, the speech-language pathologist will develop strategies and exercise to improve voice function and review good vocal hygiene.
Common Questions About Voice Problems:
What is voice?
Sound produced by the larynx (also called the ‘voice box’, located in the neck).
What is a problem voice?
- When the pitch/loudness/quality is more evident, rather than what the speaker is trying to communicate.
- The speaker might endure pain or discomfort when speaking or singing.
What can cause a voice problem?
- If someone sustains an injury that causes a paralysis of a vocal fold.
- Misuse of the voice (using a pitch level that is too high or too low).
- Abuse of the vocal chords through smoking or through exposure to chemicals or allergens, or abusive vocal behaviour (e.g., repetitive throat clearing or excessive shouting).
- Other voice disorders that occur without apparent cause are thought to be neurologic in origin.
What is an early sign of a voice problem requiring professional help?
If you have continuous hoarseness, voice change, or discomfort that lasts for more than 10 days in absence of an allergy or cold.
Swallowing
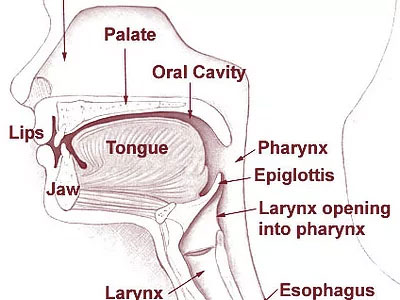
Several conditions can result in difficulty swallowing liquids and food safely.
Signs to look for include:
Drooling
Coughing while eating
A “slow” eater
Dry mouth
A speech-language pathologist can assess risks, provide exercises to strengthen oral mechanism and provide strategies for safe swallowing.
TOR-BSST©
Mary-Ellen Thompson has attended the Toronto Bedside Swallowing Screening Test (TOR-BSST©) and is certified in SLP Dysphagia Expert Training and is a TOR-BSST©-trained SLP
The TOR-BSST© offers an accurate method by which to identify stroke patients with dysphagia in both the acute and rehabilitation setting
The Sequence of the Swallow
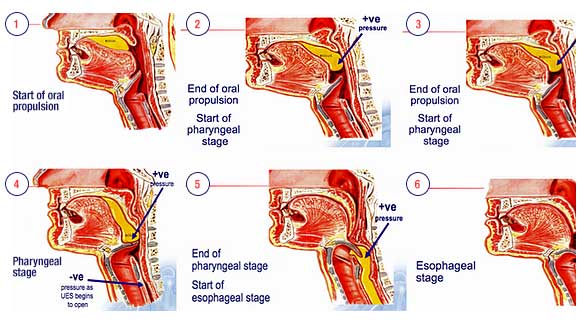
Swallowing Quotes:
“This sequence (the swallow) seems simple, yet the physiology is so complex that the fact that swallowing succeeds more than it fails… is amazing.”
– J.L. Pitcher
“A successful swallow is dependent upon the precise, coordinated movement of a large group of muscles plus a number of well-formed and healthy anatomical structures.”
– Unknown
Stroke
Stroke can result in aphasia, dysarthria, apraxia or a combination. Aphasia is defined as the loss of language. Aphasia can affect how we understand language when listening and reading, and how we transmit ideas when speaking and writing. Often, finding the right word and comprehending abstract language is difficult.
There are 300,000 Canadians living with stroke today
40% of stroke patients are living with severe disabilities
38% of stroke patients have aphasia
In Southeastern Ontario, 1,050 strokes occur per year
50,000 Canadians suffer a stroke each year
75% of people survive the initial stroke event
Strokes are the leading cause of neurological disability
Aphasia is when your brain holds your words hostage
Aphasia can mask competence
Aphasia is caused by injury to the left side of the brain
People with Aphasia take extra time to understand what is being said to them
Often times, persons with aphasia have a weakness of the right arm and leg
Dysarthria often results in slurred speech that is difficult to understand.
Apraxia results in motor planning difficulties making speech difficult to understand and resulting in extreme frustration for the speaker.
A speech-language pathologist will assess the strengths and weaknesses of those who have experienced strokes to develop a comprehensive treatment plan to improve communication, improve quality of life, and help those with lived experience reintegrate into the community.
How To Communicate With a Person Who Has Aphasia
Make sure you have the person's attention before communicating
Keep the communication simple, but adult. Never treat them like a child
Encourage people with Aphasia to be as independent as possible
Whenever possible, continue normal home activities
Do not shield people with Aphasia or be overprotective, rather, try and involve them in decision-making as much as possible
Praise all attempts to speak: eye contact, gestures, facial expressions...etc.
Office
11 Bay Bridge Road, Unit 216,
Belleville ON, K8P 3P6
Monday to Thursday : 8:30am – 6pm
Friday : 8:30am – 4pm
Phone : (613) 961-1719
